Economics with Emphasis on Microeconomics
Introduction
The field of economics allows economists, traders, and investors to study choices that insufficiency demands us to make. There are also features that permit the distinguishing of the economic approach relative to social sciences to include (Rittenberg & Tregarthen, 2017):
- A. Economists reviewing special emphasis on opportunity costs in analyzation choices;
- B. Economists making assumptions when examining choices that allow the maximization of the value of some objectives while also defining the objectives relative to self-interest;
- C. Individual maximization that enables a decision concerning a little more of something or a little less of something is best.
This research paper will examine the subject of economics with an emphasis on microeconomics. The subject of the broad areas in the field of economics, supply and demand, trading, and competitive models assist in a better understanding of the subject of economics.
Two Broad Areas in the Field of Economics
The field of economics brings with it the opportunity to learn about the elements of such things as opportunity cost, maximization, trading, investment, and choices relative to the margin of two distinct areas to include microeconomics and macroeconomics. There is the need to have an understanding of these two fields to gain insight of the field of economics.
Microeconomics focuses on choices made by the individual decision-making units in the economy concerning the consumers and business (Rittenberg & Tregarthen, 2017). These choices impact individual markets showing how and why different goods have different values, how the individuals make efficient and productive decisions and how people coordinate, cooperate and collaborate with each other. This field of microeconomics is viewed as being a complete and advanced science versus macroeconomics.
The field of macroeconomics involves focus on the impact relative to choices on the total level of economic activity inclusive of the behavior of the economy as whole, not specific companies. As an example, macroeconomics allows a view of how an increase or decrease in net exports could affect a nation's capital account. This information reveals the difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics; however, both of these processes can be used effectively to gain complete knowledge of how businesses operate and earn revenue.
Supply and Demand
According to Hayes, just like for a trader the price action is the essential part of his/her investment strategy (PriceActionHelp, 2024), supply and demand are considered to be economics basics. Supply is representative of how much the market can offer with quantity supply referencing the amount of a specified good the producer will supply when receiving a certain price. Demand references the quantity of a product or service that is desired by the buyer (Hayes, 2017). When viewing the market economy theories, demand and supply theory allocates resources in the most efficient way possible.
The law of supply demonstrates quantities sold at a certain price with the relationship seen in an upward slope. Unlike the law of demand, the higher the price, the higher the quantity supplied. This information is of importance to producers as selling a higher quantity at a higher price enables the seller to increase revenue (Hayes, 2017). Please review the graph below showing the supply relationship.
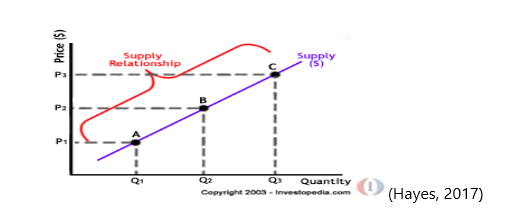
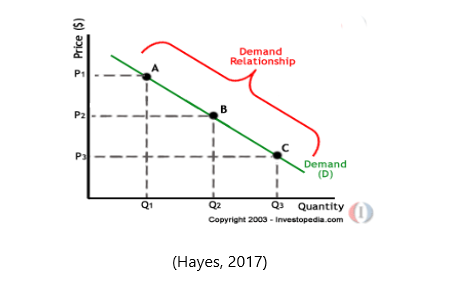
The law of demand with other factors remaining equal equates to the greater the price of the good; the fewer people will demand that good. The process lowers the quantity demanded. Shown below is a diagram showing the Demand Relationship.
Competitive Models
Competitive models allow for the emphasis on certain assumptions and expectations concerning economic behavior. The information gained from the usage of the competitive models allows better decision making. Several models could be reviewed; however, four competitive models are discussed with the first model being monopoly.
It is of importance for businesses to understand barriers to entry when considering entering a market. Barriers to entry can include several factors such as economies of scales leading to natural monopoly or control of a physical resource of patent, trademark and copyright protection ("Key Concepts and Summary: Monopoly | Microeconomics", 2017). If economies of scale exist over a huge range of output with one business supplying the whole market, no other business can enter that market without facing a cost disadvantage.
Oligopoly is a market structure with few large firms sharing an extremely concentrated market share. It is in the center of a monopoly and perfect competition, with a minimum of large firms controlling the market while offering comparable products ("Oligopoly: AP Microeconomics Crash Course Review | Albert.io", 2017). Oligopoly firms are usually large when viewing revenue, size of the business and clients. These firms compete against each other exercising fierce competition while differentiating their products and services.
Perfect competition concerns a market that has the characteristics of having a huge number of small producers or sellers offering a standardized product with the inability of individual sellers influencing pricing. This type of market also offers free entry and exit to the sellers in the markets with unnecessary non-price actions. The shortcomings of this process are that perfect competition does not provide correction for the inequity of income distribution and does not generate any public goods because of the lack of profit (Petroff, 2002).
Lastly, the monopolistic competition model is descriptive of a common market structure with businesses having many competitors with each competitor selling a product that is slightly different from other products ("Monopolistic competition", 2017). These firms make independent decisions relative to pricing and output of the product inclusive of costs. The benefit of this process is that there are no primary barriers to entry or exit ("Monopolistic competition", 2017). The monopolistically competitive firms are viewed as profit maximizers.
Conclusion
This paper has discussed economics and the two broad areas of microeconomics and macroeconomics. Emphasis has been placed on microeconomics as this field is considered to be a complete and advanced science versus macroeconomics. Supply and demand are economics basics having a concern for quantity supply sold by the seller (supply) and the higher the price of the good, the fewer people will demand that good (demand).
Competitive models emphasize economic behavior. Monopoly, oligopoly, perfect competition and monopolistic competition are descriptive of different markets. This information gives insight on how economics is used in our daily lives with the first lesson of economics being the issue of scarcity and limited resources. Another example is how money is used with a budget as a limited budget for buying one type of good causes an opportunity cost which means that there may not be money to spend on fun and entertainment (Pettinger, 2017). The study of economics is of importance to the individual, investment firms, traders, and society.
References
Hayes, A. (2017). Law of Supply and Demand: Basic Economics. Investopedia.
Key Concepts and Summary: Monopoly | Microeconomics | Trading. (2017). Courses.lumenlearning.
Monopolistic competition. (2017). Stock Market Picks Online.
Oligopoly: AP Microeconomics Crash Course Review | Albert.io. (2017). Albert Blog.
Petroff, J. (2002). MicroeconomicsPerfect Competition. Peoi.
Pettinger, T. (2017). Applying economics and technical analysis in everyday life. Economicshelp.
PriceActionHelp (2024). Helping traders and investors forecast the future price action of a financial instrument. PriceActionHelp.com
Rittenberg, L., & Tregarthen, T. (2017). Principles of Microeconomics and Investing 1.0 | FlatWorld. FlatWorld.